Ship breaking, the process of dismantling decommissioned ships to recycle their parts and materials, plays a crucial role in the global economy. However, it’s a practice fraught with challenges, environmental concerns, and safety risks. In this blog, we’ll explore the ship breaking industry, its importance, the challenges it faces, and the innovations driving safer and more sustainable practices.
Definition and Process:
Ship breaking involves the disassembly of ships into their component parts, including steel, machinery, and other materials, which are then recycled or repurposed.
The process typically includes beaching the ship, stripping valuable components, cutting down the structure, and finally, recycling the materials.
Historical Context:
The practice dates back centuries but has evolved significantly, with modern techniques improving efficiency and safety, yet also raising environmental and ethical issues.
Economic Benefits:
Ship breaking is a major source of recycled steel, which reduces the need for new steel production, saving energy and reducing carbon emissions.
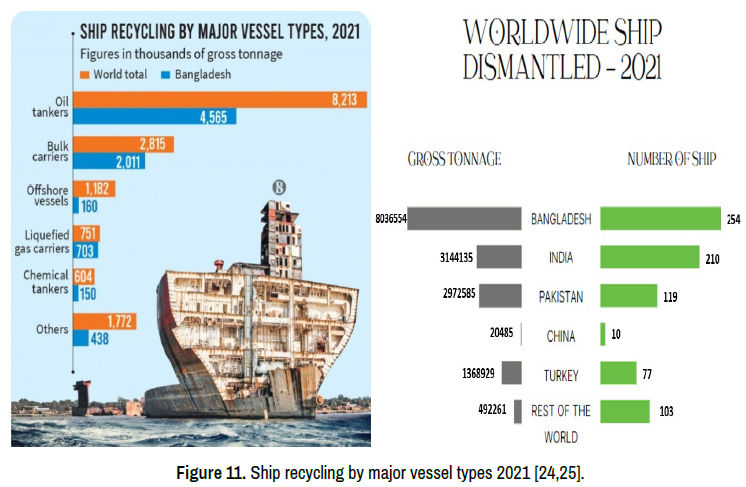
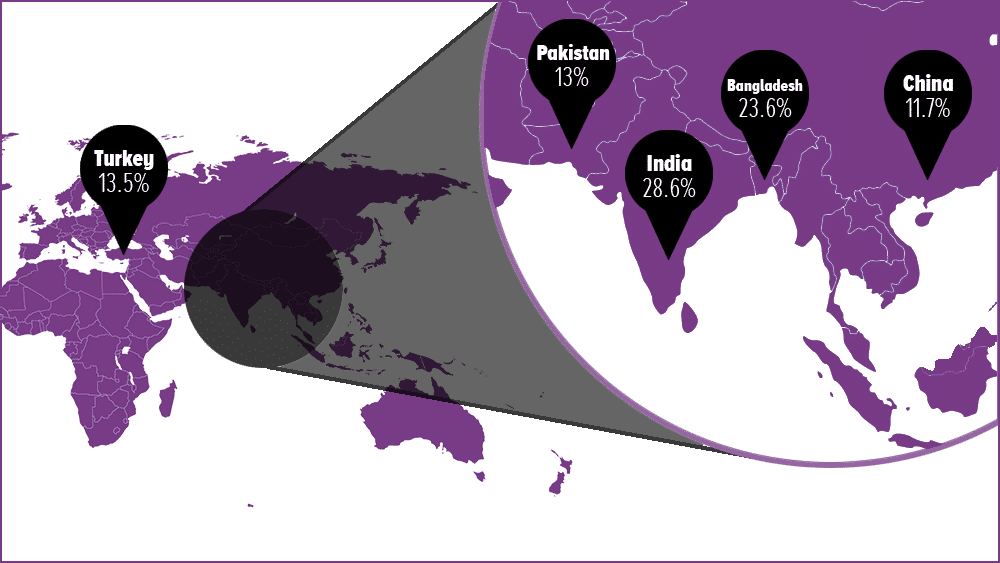
It provides employment opportunities, especially in countries where ship breaking is a significant industry, such as Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan.
Resource Recovery:
Ships contain valuable materials like steel, aluminum, copper, and other metals, as well as machinery and equipment that can be reused in various industries.
End-of-Life Management:
With an increasing number of aging vessels, ship breaking is essential for managing the end-of-life phase of ships, ensuring that they are not left abandoned in ports or at sea.
Environmental Concerns:
Pollution: The dismantling process can release hazardous materials like asbestos, heavy metals, and oil residues into the environment, particularly when ships are beached and broken down in coastal areas.
Waste Management: Proper disposal and treatment of toxic waste generated during ship breaking is often lacking, leading to severe environmental degradation.
Safety Hazards:
Worker Safety: Ship breaking is one of the most dangerous jobs in the world, with risks including exposure to toxic materials, falling objects, and accidents during cutting and lifting operations.
Lack of Regulation: In some regions, ship breaking occurs with minimal oversight, leading to poor working conditions and inadequate safety measures.
Ethical Issues:
Labor Rights: Many ship breaking yards employ low-wage workers, including children, under unsafe conditions, raising significant ethical concerns.
Regulatory Evasion: Some ship owners choose to sell their vessels to regions with lax environmental and labor regulations, often referred to as “flag of convenience” practices.

Green Ship Recycling:
Certification and Compliance: Initiatives like the Hong Kong International Convention for the Safe and Environmentally Sound Recycling of Ships aim to improve industry standards and ensure safer, greener ship recycling practices.
Technology Integration: Advanced cutting and lifting technologies, as well as automated processes, are being introduced to minimize human risk and environmental impact.
Offshore Ship Recycling:
Instead of beaching ships, some companies are moving towards offshore or dry dock ship breaking, where better containment of hazardous materials and safer working conditions can be maintained.
Circular Economy and Upcycling:
The ship breaking industry is exploring ways to not only recycle but also upcycle ship components, giving them a new life in different industries, thereby reducing waste and promoting a circular economy.
Regulatory Developments:
Increased global attention is leading to stricter regulations and improved oversight, pushing the industry towards more responsible practices.
The adoption of international agreements, such as the Basel Convention and the European Union Ship Recycling Regulation, is expected to drive further change.
Sustainability Focus:
As the world moves towards more sustainable practices, the ship breaking industry is likely to face pressure to adopt greener methods, improve worker safety, and reduce its environmental footprint.
Innovation and Collaboration:
Collaboration between governments, ship owners, and environmental organizations will be key in driving innovations that make ship breaking safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly.
The ship breaking industry, while crucial for resource recovery and economic development, faces significant challenges in terms of safety, environmental impact, and ethics. However, with ongoing innovations, stricter regulations, and a growing focus on sustainability, the future of ship breaking could see a transformation towards safer and more responsible practices. As global awareness increases, it is imperative that all stakeholders work together to ensure the industry evolves in a way that benefits both people and the planet.

April 10, 2023

March 30, 2023
We are committed to providing exceptional services in metal recycling, fabrication, and waste management. With a focus on sustainability and efficiency, we transform waste into valuable resources and deliver high-quality products.
Sunday Hub, 401, Aamba Talavadi, Gayatri Nagar, Katargam, Surat, Gujarat 395004
+91 889 680 1212
hr@al-rasavi.com
Comments (2)
Karan SinghNovember 29, 2021
The ship-breaking industry plays a crucial role in resource recovery, but it's essential to prioritize worker safety and environmental protection.
Abhishek KeshriJanuary 03, 2022
Fascinating to see how ship breaking contributes to the circular economy! Recycling and reusing materials from old ships is a sustainable approach we need more of.